Deploying and running a redpesk image for the BeagleBoard BeaglePlay board
The BeaglePlay is a Linux computing designed board using a TI Sitara AM625 system-on-chip. Its very interesting feature is the BeagleConnect® technology whichs allows a connection over the sub-1GHz IEEE 802.15.4 wireless network to a BeagleConnect® Freedom up to 1km away. Deploying a redpeskOS image on this kind of board consists of copying a disk image on an SDcard. See the BeaglePlay specification on the BeagleBoard website.
Download images
See Download Images section.
Download BeaglePlay image from command line
Create a directory to download the image:
mkdir ~/redpeskimage
cd ~/redpeskimage
Then download the latest redpesk OS image with this command:
wget -r -nd -nc --no-parent --accept-regex='redpesk.*smack.*\.(bmap|xz|sha256)' --reject-regex '(image\.raw|ova|index)' 'https://download.redpesk.bzh/redpesk-lts/batz-2.1-update/images/smack/minimal/aarch64/beagleplay/'
Control the image integrity
Before doing anything, please control the integrity of the downloaded redpesk image. Example:
sha256sum -c redpesk*.tar.xz.sha256
redpesk*aarch64*.tar.xz: OK
Copying the image on your SD card
Plug your SD card and find it (be sure it is unmounted)
Copy the correct device path using the command below. It should be a hotplug device.
lsblk -dli -o PATH,VENDOR,TYPE,HOTPLUG,MODEL
DEVICE_TO_COPY='/dev/<hotplug_device>' #in the example it is /dev/sdc
Example:
$ lsblk -dli -o PATH,VENDOR,TYPE,HOTPLUG,MODEL
PATH VENDOR TYPE HOTPLUG MODEL
/dev/sda ATA disk 0 WDC_WD10SPZX-08Z10
/dev/sdc TS-RDF5 disk 1 SD_Transcend #MYSDCARD
/dev/nvme0n1 disk 0 LITEON T11 512
DEVICE_TO_COPY=/dev/sdc
Or if only one device is hotpluggable on your computer:
# need jq
DEVICE_TO_COPY=$(lsblk -dlJ -o PATH,VENDOR,TYPE,HOTPLUG,MODEL | jq -r '.blockdevices[] | select(.hotplug == true).path')
echo $DEVICE_TO_COPY
Umount if needed
lsblk $DEVICE_TO_COPY
# need to umount each partition
sudo umount <part*>
Example:
$ lsblk /dev/sdc
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sdc 8:32 1 14.6G 0 disk
├─sdc1 8:33 1 501M 0 part /run/media/iotbzh/0409-3A02
├─sdc2 8:34 1 1G 0 part /run/media/iotbzh/cd3c87ec-1011-4832-aef3-6be0ed3d3748
└─sdc3 8:35 1 2.5G 0 part /run/media/iotbzh/4e508264-8ce2-447f-a829-e4c31ea20047
$ sudo umount /run/media/iotbzh/*
Flash sdcard
Prerequisites: device is plugged in, found, unmounted
- Extract the image first
tar xJf redpesk*.tar.xz - Flash it using
ddsudo dd if="Redpesk-OS.img" of=$DEVICE_TO_COPY bs=4M status=progress - Or using bmaptool
bmaptool copy "Redpesk-OS.img" $DEVICE_TO_COPY
TIPS: Once you are used to flash your image, you could do it much faster in one single step using
bmaptoollike this:bmaptool copy "https://download.redpesk.bzh/redpesk-lts/batz-2.1-update/images/smack/minimal/aarch64/beagleplay/image.raw.tar.xz" $DEVICE_TO_COPYThis will download, control integrity and flash the latest redpesk OS image on your device.
Hardware DIP switch configuration
Integrated into the PCB, a DIP switch is generally present to allow you to choose between different boot mode.
There isn’t any DIP switch on the BeaglePlay board.
Connect to the BeaglePlay board
- Plug in the SD card into the board.
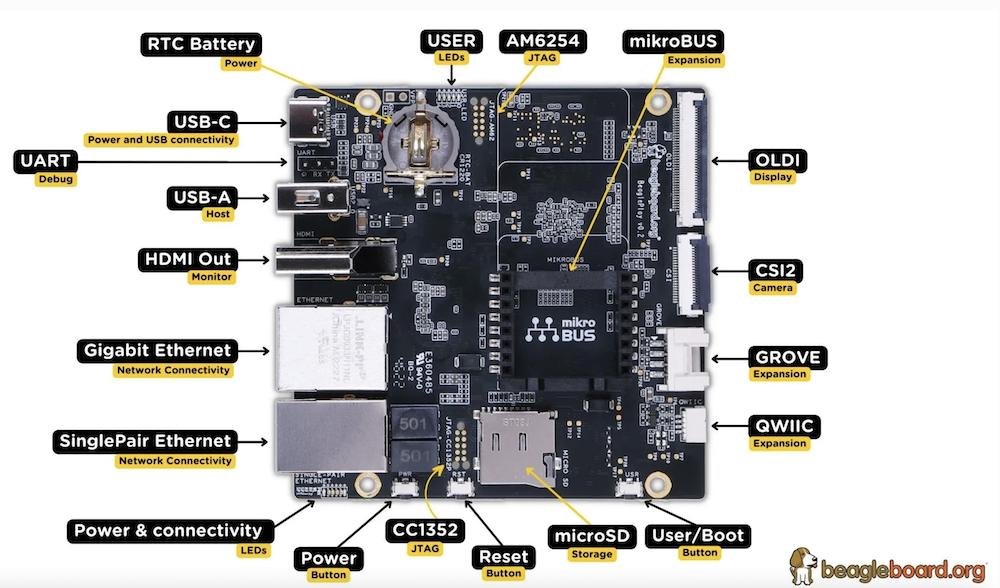
- Connect the USB-UART cable following the three pins beside the SD card socket.
- By default, the board will boot to the eMMC. To boot to the SD card, you need to hold the
USRbutton while you powered the board by USB-C. Or by default, the bootloader stored on the eMMC is able to jump to the SD card if you have an extlinux configuration file in your/bootpartition. Please refer to this documentation for more details. - Power on the board (USB-C cable).
use
dmesgto see the name of the USB plugged[ 7.567111] usb 1-2.1.2: pl2303 converter now attached to ttyUSB1 -
Use picocom (or minicom depending on your tools!)
sudo picocom -b 115200 /dev/ttyUSB1NOTE: Default root password is
root. -
Getting the address of the board to be able to use a SSH connection
Connect an Ethernet cable between computer and the BeaglePlay.
#on board ip -c a# on computer ssh root@<ip_board>
Installing a package
Your board is now ready to boot redpesk OS. You can install any packages and/or your own packages.
Please refer to section Application deployment for more details.