Running/Testing
When in the need of a quick feedback loop, the config file should be used as shown below. For production, the resource binding system should be used: the spawn-binding is installed as a resource binding which cannot be launched on its own; another binding, which is launch-able by the framework facilities, provides a configuration to the spawn-binding. See more details about resource bindings here.
Requirements
- you should have a valid afb-binder install.
- you should write or copy a sample spawn-config.json (see in spawn-binding’s repo
- you should known the path to
spawn-binding.so - you need a test client
- afb-client as a command line interface
- afb-ui-devtools as a graphical user interface (web app, test with a browser)
Run spawn-binding samples
afb-binder --binding=/usr/redpesk/spawn-binding/lib/spawn-binding.so:./spawn-basic-config.json -vvv
Note: –binding should point to where your spawn-binding.so is installed, the path after
:should point to a valid JSON config
Depending on what commands you are trying to run and with which
containerization options, you may need to add sudo before the command
so that the binding has the necessary privileges.
HTML5 test
Open binding UI with browser at [host]:[port]/devtools/index.html in your browser address bar.
For example: localhost:1234/devtools/index.html for a binding running on localhost, on port 1234.
You should see a page as the one below fitting your configuration. To activate a command simply click, select a sample and sent.
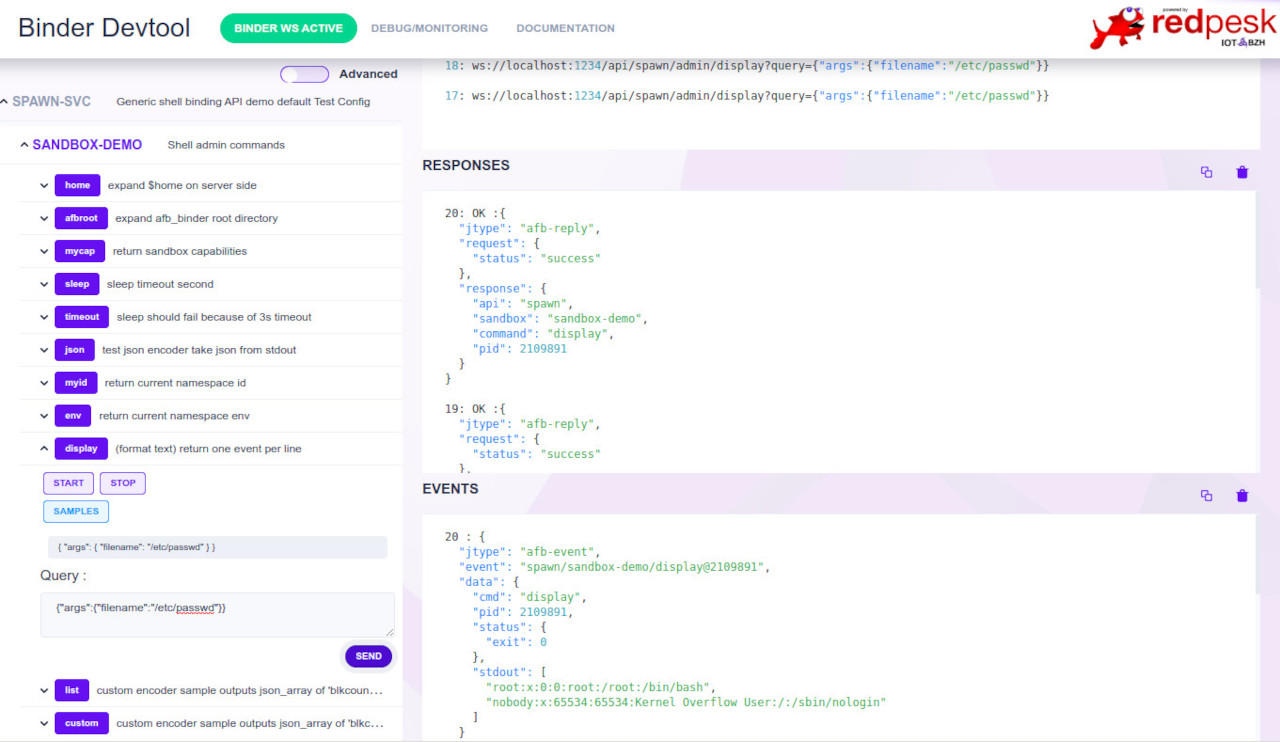
Command line test
Connect afb-client to spawn-binding service
afb-client --human ws://localhost:1234/api
Note: depending on afb-client version you may have no prompt. Use
simple pingto assert spawn binding is alive !!!
Basic commands
spawn admin/myid
spawn admin/env
spawn admin/cap
spawn is what ever api name your have chosen in your config.json. Start is the default action, also spawn admin/myid is equivalent to spawn admin/myid {“action”:”start”}.
Passing arguments from query to CLI
Api query takes args from the client as a json-object compose of {“name”:”value”} tuples.
spawn admin/list {"args":{"dirname":"/etc"}}
spawn admin/list {"args":{"dirname":"/home"}}
spawn admin/display {"args":{"filename":"/etc/passwd"}}
Each argument passed into query args replaces corresponding %name% in binding config.json. In following example json query argument {“timeout”: value} is passed to sleep command.
config: "exec": {"cmdpath": "/bin/sleep", "args": ["%timeout%"]}
query: {"action":"start","args":{"timeout":"180"}}
start: sleep 180;
- mandatory argument: %argument% (abort the request when missing)
- optional argument: ?argument? (silently replaced by “” when missing)
Advanced tests
Check for conf.d/project/etc for more advance samples.
Note: depending if you start spawn-binding in a privilege mode or not, some behavior may change. For example “user/group” or “capacity” required to start the binder in admin mode with sudo.
- NOTICE: [API spawn] sandboxParseAcls: [ignoring user/group acls] sandbox='sandbox-demo' no uid/gid privileges ignoring user='"daemon"' group='"dialout"' [/home/fulup/spawn-binding/src/- spawn-sandbox.c:510,sandboxParseAcls]
- NOTICE: [API spawn] [capability ignored] sandbox='sandbox-demo' capability='KILL[set]' (sandboxParseOneCap)
- NOTICE: [API spawn] [cgroups ignored] sandbox=sandbox-demo user=1000 not privileged (sandboxLoadOne)
Warning if you load multiple file double-check that they register different APIs name. Your HTML5 interface should reflect
Testing with GDB
When testing with GDB you should add –trap-faults=no in order to prevent afb-binder from trapping errors.
gdb --args afb-binder --binding=/usr/redpesk/spawn-binding/lib/spawn-binding.so:./spawn-basic-config.json -vvv --trap-faults=no
Testing namespace
Namespace allows to create a fake root filesystem that only expose the minimal necessary resources. Unfortunately depending on your restriction the process may not even start, with no-log to help debugging the situation.
For a quick namespace test, start spawn-binding with spawn-sample-nspace.json. Then use spawn/admin list api/verb to explore your namespace.
afb-binder --binding=/usr/redpesk/spawn-binding/lib/spawn-binding.so:./etc/spawn-sample-nspace.json -vvv
Namespace can a tricky to debug. In case of doubt add {"verbose":1} to query argument list, this will push within your command stderr the bwrap equivalent command. You may then copy/paste the command line and replace you command with “bash” to explore in interactive mode your namespace.
Testing formatting
spawn-binding support 3 builtin formatting options. Encoder formatting is enforced for each command within config.json. Default encoder is “DOCUMENT” and it cannot not be change at query time. Check spawn-sample-encoders.json for example. If you need the same command with multiple formatting, then your config should duplicate the entry with different uid.
Exposing spawn API as AFB micro-service
In order to make spawn-binding api accessible from other AFB micro-service you simply export the API with –ws-server=unix:/path/apiname as you would do for any other AFB micro-service. The exposed API may later be imported with –ws-client==unix:/path/apiname by any afb-binder that get corresponding privileges. Note: when exposing an API locally it is a good practice to remove TCP/IP visibility with –no-httpd
# note than --ws-server=unix exported API should match with selected config.json
afb-binder --binding=/usr/redpesk/spawn-binding/lib/spawn-binding.so:./etc/spawn-simple-config.json -vvv --no-httpd --ws-server=unix:/run/user/$UID/simple
Direct unix socket API can be tested with –direct argument
# note that when using direct api, apiname should not be added to the request
afb-client --direct unix:/run/user/$UID/simple
> ping
> admin/env
Autoload/Autostart
spawn-binding supports an ‘autoload’, any action in this sections will be tried at binding starup time.
"onload": [
{
"uid": "vpn-autostart",
"info": "create VPN interface (reference https://www.wireguard.com/quickstart)",
"action": "api://autostart#vpn-start"
}
],
wireguard-autostart.json provide a small example to start a wireguard VPN.
To run the test.
- Install ‘wireguard-tools’ to get ‘wg-quick’ helper.
- Start ‘wireguard-autoconfig.sh’ to create a test config into /etc/wireguard/spawn-binding.conf
- Check with
sudo wg-quick up spawn-bindingthat your config works. - Start ‘spawn-binding’ in privileged mode with
sudo AFB_SPAWN_CONFIG=../conf.d/project/etc/wireguard-autostart.json afb-binder --name=afb-spawn --binding=package/lib/afb-spawn.so --verbose
caching events
spawn-binding is an afb-controller and may on event reception execute internal/external API. For external action you should use –ws-client=xxx to import the api within spawn-binding context. Note that to execute an external API you also need corresponding privileges.
"events": [
{
"uid": "monitor/disconnected",
"info": "call log function on monitor/disconnect event detection",
"action": "api://autostart#vpn-log"
}
],