Project secrets
Introduction
redpesk CI/CD operations might need sensitive information, called secrets, to complete work. This sensitive information can be items like API tokens or private keys. Secrets are stored in a secured service (vault) that is part, or not, of the redpesk factory.
A secret is a key, value data. The key name (KEY_NAME) is used to refer
the secret in various parts: eg. git sources URL, external specfile URL or secret
injection in source code, …
Syntax to refer a secret is ${{secrets.KEY_NAME}} where KEY_NAME is the name
of your secret. When special ${{secrets.KEY_NAME}} keyword is detected by the
redpesk factory, during for example the application source clone step; a mechanism
automatically retrieves the secret through vault regarding the key name in
order to replace it by the secret value.
Secrets can be used in various steps of your application or image build process.
Here are some steps where secrets can be used in the following application settings:
| Where | WebUI view | rpcli command or line example |
|---|---|---|
| source URL to refer an access token | Project > Application > Settings : Source URL | rpcli application update my-app --source-url 'https://${{secrets.myToken}}@gitlab.com/myrepo' |
| external specfile URL | Project > Application > Settings : Spec file, External URL | rpcli application update my-app --specfile-type external_url --specfile-location 'https://${{secrets.myToken}}@gitlab.com/myrepo/-/raw/master/my-app.spec' |
| some application services | Project > Application > Settings : Application Services, Import external SRPM | rpcli application update my-app --service '{"parameters":{"url":{"value":"https://${{secrets.myToken}}@gitlab.com/myrepo/-/raw/master/my-app.spec"}}} |
| in specfile SOURCE tag | Project > Application > File Manager : specfile | SOURCE1: https://${{secrets.myToken}}@server/file.zip |
| in specfile | Project > Application > File Manager : specfile | in sections or in macros for example: %build MY_SECRET=${{secrets.SECRET1}} make build
|
| in kickstart url | Project > Image > My Image > Advanced settings: Kickstart git repo URL | rpcli application update my-image --ks-url 'https://${{secrets.myToken}}@gitlab.com/myrepo/-/raw/master/my-ks.ks' |
| in kickstart | in git repository | in some parameters of kickstart commands: for example:rootpw --iscrypted ${{secrets.MYPASSWORD}}or in sections for example: %postecho ${{secrets.myappcrt}} > /etc/pki/myapp/app.crt%end
|
Secrets are defined in the context of a project’s environment, allowing
different secret values for different project environments.
In other words, the same secret key (eg. {{$secrets.my_api_token}}) will be
set to :
- value
Awhen building an application in the context of project’s environment namedprod - value
Bwhen building an application in the context of project’s environment nameddev
A secret cannot be updated, if you need to change the secret value, you must first delete the secret and re-create it with the new value.
List existing secrets
WebUI
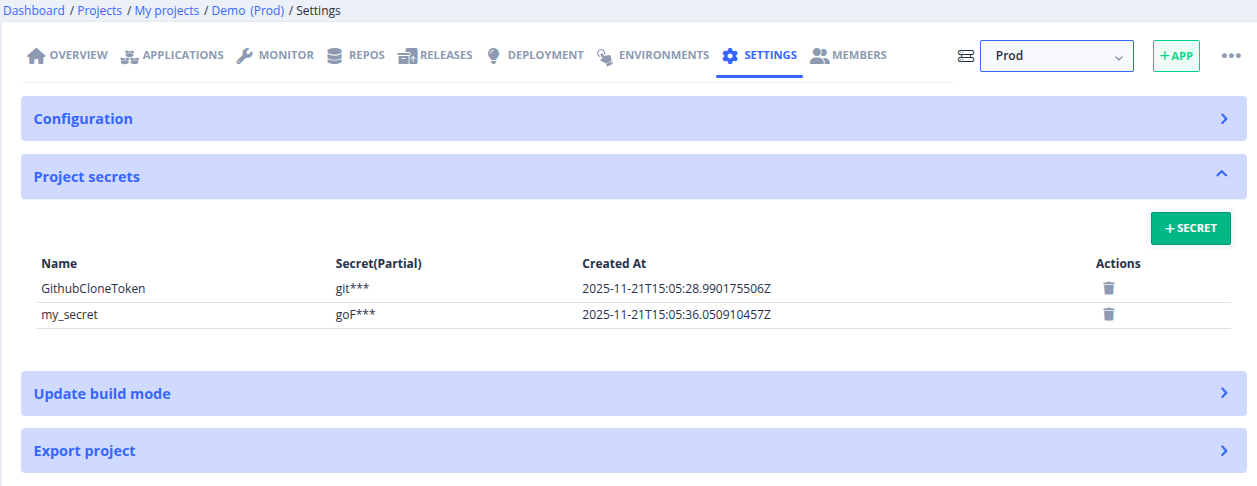
Browse to your project settings view and open the Project secrets section.
Note that secrets are defined per project’s environment, so take care to select
the right environment.
WARNING: in factory release Armel 1.10, secrets are fully independents from one environment to an other. That means you need to create manually the same secret key for each environment
redpesk-cli
Use projects secrets list command following by your project name (here ‘demo’) :
$ rpcli projects secrets list demo
Key Created_at
GithubCloneToken 2025-11-21 15:05:28.990175506 +0000 UTC
my_secret 2025-11-21 15:05:36.050910457 +0000 UTC
Create
Secrets management is per project’s environment, so take care to select the right environment.
Note: only manager or developer roles can create secrets.
WebUI
To create a secret, browse to your project settings view and open the
Project secrets section. Then click on the + Secret button and fill the
secret name and value fields.

redpesk-cli
Use projects secrets add command:
$ rpcli projects secrets add demo my_secret --value 1234
-- Secret creation requested by user --
Request the factory to add the secret... [OK]
Delete
Secrets management is per project’s environment, so take care to select the right environment.
Note: only manager or developer roles can delete secrets.
WebUI
Browse to your project settings view and open the Project secrets section and use trash icon to delete it.
redpesk-cli
Use projects secrets delete command:
$ rpcli projects secrets delete demo my_secret
-- Secret deletion requested by user --
Request the factory to delete the secret... [OK]
Usage within localbuilder
Localbuilder allows to ease development of application packaging (eg. specfile
development, tuning).
For security reasons, secrets (and specifically secrets value) cannot be automatically
retrieved during local package initialization (command: rpcli local package init).
So you need to set manually secrets value following process describe in localbuilder project packaging chapter.