Main redpesk recovery features
General principles
During industrial use in an embedded context, you may encounter a corrupted root filesystem, a broken Linux kernel or issues with necessary systemd base services.
If your system fails to boot for any reason, it may be useful to boot it into recovery mode.
This mode only loads basic services as root and can repair your system choosing some default actions.
On redpesk OS, this feature enables the recovery of the root file system in different ways:
- by a default image which is stored on the
/recoverypartition (eMMC/SD card) - by a USB key (the
backup.tar.gzimage must be stored on the USB key’s root)
Note: The USB key might be changed to another device depending on your needs.
A Linux kernel watchdog could be implemented to avoid booting all the time in the recovery mode.
Restoring essential boot parts
redpesk OS /recovery partition
On a default redpesk OS image (please refer here for partitioning details), the /recovery partition contains these items:
/run/media/iotbzh/recovery
|-- backup.tar.gz -> tarball copy of the rootfs (~250Mo for recovery)
|-- imx8mn-compact-5.4.47-24.solidrun.edge.gateways.bsp.rpbatz.aarch64.dtb -> dtb
|-- imx8mn-compact.dtb -> dtb (symbolic link)
|-- initramfs.img -> initramfs made by dracut
`-- recovery.img -> kernel Image
Restoration mechanism
As shown in the following illustration, the recovery mode restores the kernel image, the device tree blob and the rootfs archive when activated.
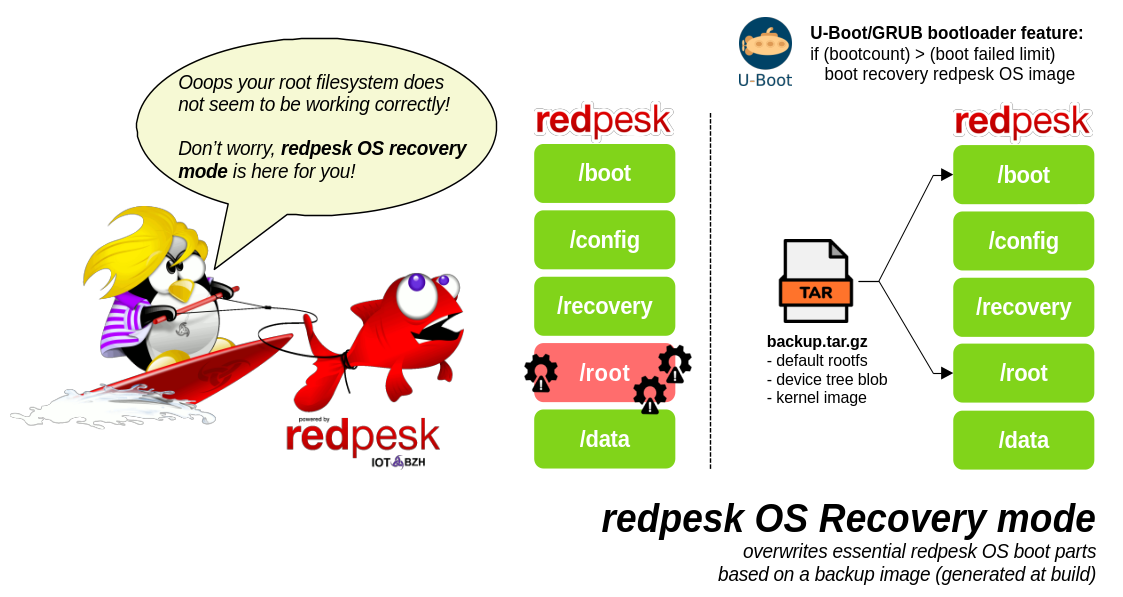
These components have been generated during the image build. It is specified by dracut-redpesk-recovery.
This package contains dracut configuration recipes to build the initramfs dedicated for recovery mode booting. More details in this section.
Initramfs creation
To create the initramfs dedicated for redpesk OS, dracut uses configuration files. They are installed in the /etc/dracut.conf.d/redpesk/ directory thanks to features/initramfs.ks.
There are dracut modules too which are available in /usr/lib/dracut/modules.d/99recovery.
In output, an image must be converted to U-Boot ramdisk in order to be readable by U-Boot.
#Create and correct dracut initramfs file to be loaded into U-Boot
#This initramfs will be used for recovery mode and will then but installed into recovery partition mounted in /recovery
%packages
dracut-redpesk-recovery
%end
%post --erroronfail --log /tmp/post-initramfs.log
dracut -f --no-kernel --confdir="/etc/dracut.conf.d/redpesk/" /tmp/initramfs.img
if [[ `rpm -E %{_arch}` == "aarch64" ]]; then
mkimage -A arm64 -O linux -T ramdisk -C gzip -d /tmp/initramfs.img /recovery/initramfs.img
rm -f /tmp/initramfs.img
else
mv /tmp/initramfs.img /recovery/initramfs.img
#Re-generate grub2 entries with recovery initramfs
grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/efi/EFI/redpesk/grub.cfg
fi
#Remove pkg only installed for initramfs generating
dnf remove -y dracut-redpesk-recovery
%end
If you want to see our Dracut recipes used for the redpesk OS recovery mode, you can find here the sources.
backup.tar.gz creation
The redpesk OS backup is just an archive of the root filesystem. It is created by the features/factory_backup.ks kickstart.
tar -cvpzf $dir/backup.tar.gz \
--exclude=./boot/firmware/* \
--exclude=./boot/efi/* \
--exclude=./recovery/* \
--exclude=./data/* \
--exclude=./config/* \
--exclude=./dev/* \
--exclude=./proc/* \
--exclude=./run/* \
--exclude=./sys/* \
.
It will override the /root partition during the restoration.
kernel & dtb copy
At each redpesk OS image build, the kernel and the dtb are copied to the recovery partition. It is done by the features/recovery.ks kickstart.
%post --erroronfail --log /tmp/post-recovery.log
if [[ `rpm -E %{_arch}` == "aarch64" ]]; then
cp /boot/Image /recovery/recovery.img
cp /boot/*.dtb /recovery/
elif [[ `rpm -E %{_arch}` == "x86_64" ]]; then
cp /boot/vmlinuz*x86_64 /recovery/recovery.img
else
echo "WARN: recovery not supported for this arch."
fi
sed -i '/recovery/d' /etc/fstab
%end
Recovery from U-Boot (redpesk OS - aarch64)
A U-Boot feature is the boot count limit.
Enabled by CONFIG_BOOTCOUNT_LIMIT, it allows the detection of multiple failed attempts to boot redpesk OS. After a power-on reset, the bootcount variable will be initialized to 1, and each reboot will increment the value by 1.
Typically for redpesk OS, the recovery mode is selected when the bootcount variable is greater than the bootcount limit.
When this is the case, U-Boot doesn’t use bootcmd but altbootcmd (such as alternative boot) which goes to the recovery initramfs loading. More details in this example here.
Recovery from GRUB (redpesk OS - x86_64)
For x86 boards, another GRUB entry is created by following this configuration:
menuentry "redpesk Recovery mode" {
insmod part_gpt
insmod ext2
set reco='hd0,3'
linux ($reco)/recovery.img ro security=smack console=ttyS0,115200 rhgb audit=0
initrd ($reco)/initramfs.img
}
You have the choice of the boot way during the GRUB boot selection.