redpesk OS recovery usages
Requirements
recovery-tools-binding
By default, the redpesk OS recovery feature isn’t activated so it requires the installation of recovery-tools-binding-scripts on your redpesk OS image. This package contains necessary scripts needed for recovery mode activation.
dnf install recovery-tools-binding-scripts
rpm -ql recovery-tools-binding-scripts
/usr/redpesk/recovery/scripts
/usr/redpesk/recovery/scripts/check-update.sh
/usr/redpesk/recovery/scripts/get_board_data.sh
/usr/redpesk/recovery/scripts/restore_backup.sh
It is possible to avoid the recovery-tools-binding-scripts installation on your target. More details here.
Example on a supported board
For example, you want to enable the recovery mode on the SolidRun SolidSense N8 Edge Gateway board. Some others packages are required like spawn-binding but they are automatically installed as dependencies with the recovery-tools-binding package. So, as explained above, you first need to install recovery-tools-binding-scripts on the board:
[root@localhost ~]# dnf install recovery-tools-binding-scripts
Updating Subscription Management repositories.
Unable to read consumer identity
This system is not registered with an entitlement server. You can use subscription-manager to register.
Redpesk BSP solidrun-edge-gateways-bsp Update b 117 kB/s | 119 kB 00:01
RedPesk Middleware batz-2.1 Update - aarch64 274 kB/s | 295 kB 00:01
RedPesk Baseos batz-2.1 Update - aarch64 1.4 MB/s | 6.5 MB 00:04
RedPesk Config 899 B/s | 903 B 00:01
Dependencies resolved.
============================================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
============================================================================================================
Installing:
recovery-tools-binding-scripts aarch64 1.0.3-12.redpesk.common.rpbatz redpesk-middleware-update 421 k
How to enable the recovery mode
Please note that the following process can be adapted to your needs on demand.
Checking recovery environment (optional)
- Get recovery redpesk OS version
/usr/redpesk/recovery/scripts/get_board_data.sh --recovery
{"recovery": {
"PRETTY_NAME":"redpesk Linux batz LTS",
"VERSION":"batz LTS",
"VERSION_ID":"2.0.0",
}}
- Get U-Boot settings for recovery
/usr/redpesk/recovery/scripts/get_board_data.sh --uboot
## Error: "upgrade_available" not defined
{"boot_flags": {
"limit":"3",
"counter":"",
"upgrade_available":"",
}}
Activating recovery mode
You must enable the recovery tools by doing the following action:
/usr/redpesk/recovery/scripts/check-update.sh -s=0,1
/usr/redpesk/recovery/scripts/check-update.sh -p
=========================
BOOT COUNT FLAGS
-------------------------
BOOTLIMIT : 3
BOOTCOUNT : 1/3
UPGRADE : 1
=========================
To understand what it does, the script adds the upgrade_available variable to U-Boot’s environment by using fw_setenv to write to /var/lib/rp-recovery/uboot-env.config. Please refer here for more U-Boot details.
It has added the upgrade_available variable into the U-Boot’s environment config:
soc_type=imx8mn
upgrade_available=1
usb_boot=usb start; if usb dev ${devnum}; then devtype=usb; run scan_dev_for_boot_part; fi
vendor=solidrun
Rebooting to recovery mode
The system will automatically go into recovery mode the third time it boots if you activate the recovery mode. Indeed, the BOOTCOUNT variable is increased at each boot by the U-Boot bootloader. The limit to its variable is normally 3 that’s why you will go into recovery mode with this value.
Normal Boot
Warning: Bootlimit (3) exceeded. Using altbootcmd.
Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0
switch to partitions #0, OK
mmc1 is current device
Scanning mmc 1:1...
Found U-Boot script /altboot.scr
504 bytes read in 10 ms (48.8 KiB/s)
## Executing script at 44100000
Boot into recovery mode...
37743 bytes read in 17 ms (2.1 MiB/s)
29528576 bytes read in 1743 ms (16.2 MiB/s)
30232962 bytes read in 1267 ms (22.8 MiB/s)
Here you are into the recovery mode!
pre-mount:/# cat /etc/os-release
NAME="redpesk Linux"
VERSION_ID="2.0.0"
VERSION_CODENAME="batz"
ID="redpesk"
ID_LIKE="rhel fedora centos"
PLATFORM_ID="platform:rpbatz"
ANSI_COLOR="0;31"
CPE_NAME="cpe:/o:redpesk:centos:batz"
HOME_URL="https://redpesk.bzh/"
BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugs.redpesk.bzh"
redpesk_MANTISBT_PROJECT="redpesk-batz"
redpesk_MANTISBT_PROJECT_VERSION="batz"
ARCH="aarch64"
BUILD_DATE="2024-02-26 06:03:41"
VERSION="batz LTS dracut-057-21.git20230214.baseos.rpbatz"
PRETTY_NAME="redpesk Recovery v0.9.5-5.redpesk.core.rpbatz Linux batz LTS dracut-057-21.git20230214.baseos.rpbatz "
DRACUT_VERSION="057-21.git20230214.baseos.rpbatz"
redpesk OS recovery modes
You can access the recovery-tools-binding web interface on the network interface of your board, port 8080:
If you don’t have any backup.tar.gz on both factory and USB modes, you can only choose a reboot without any recovery actions.
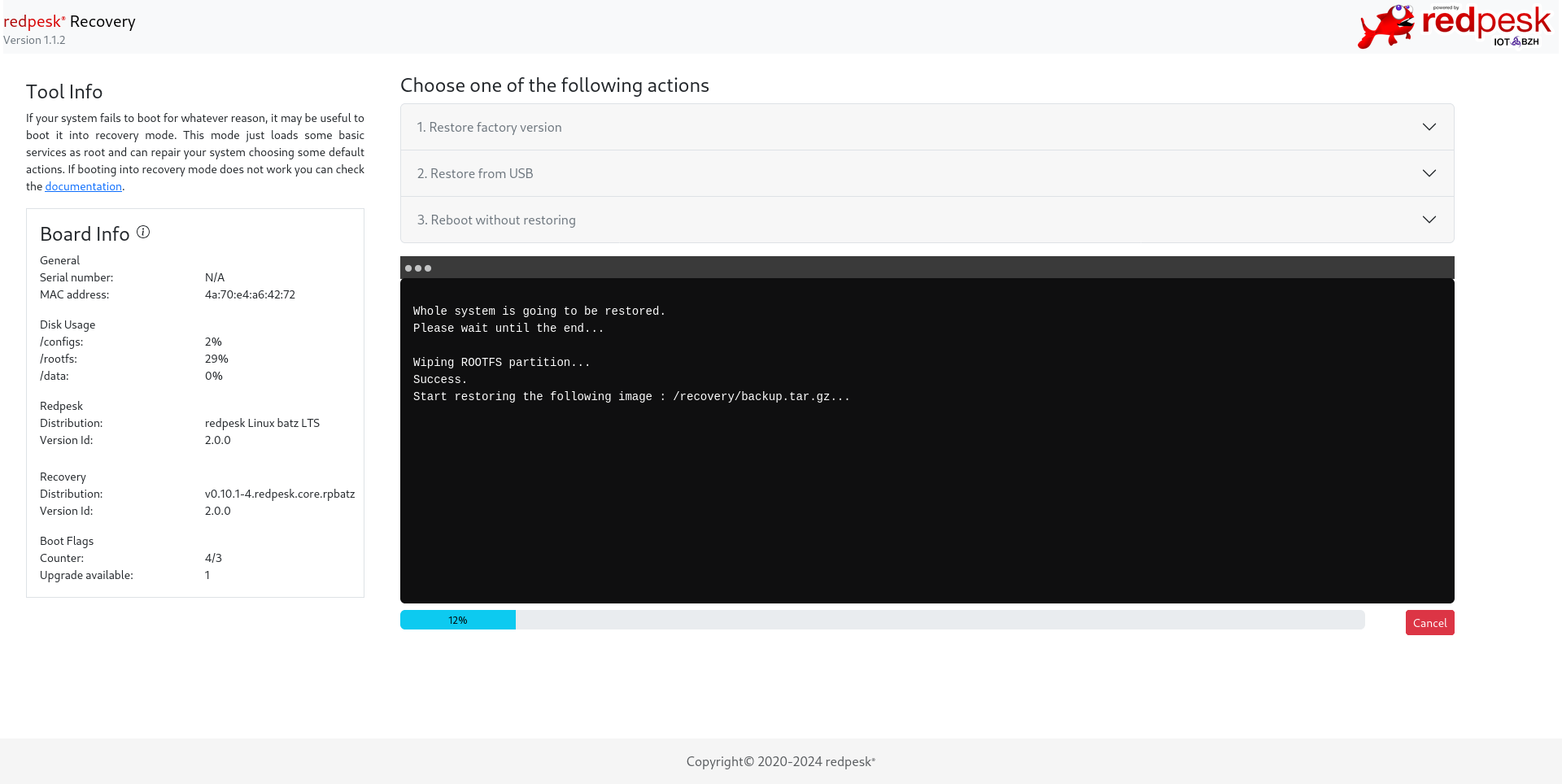
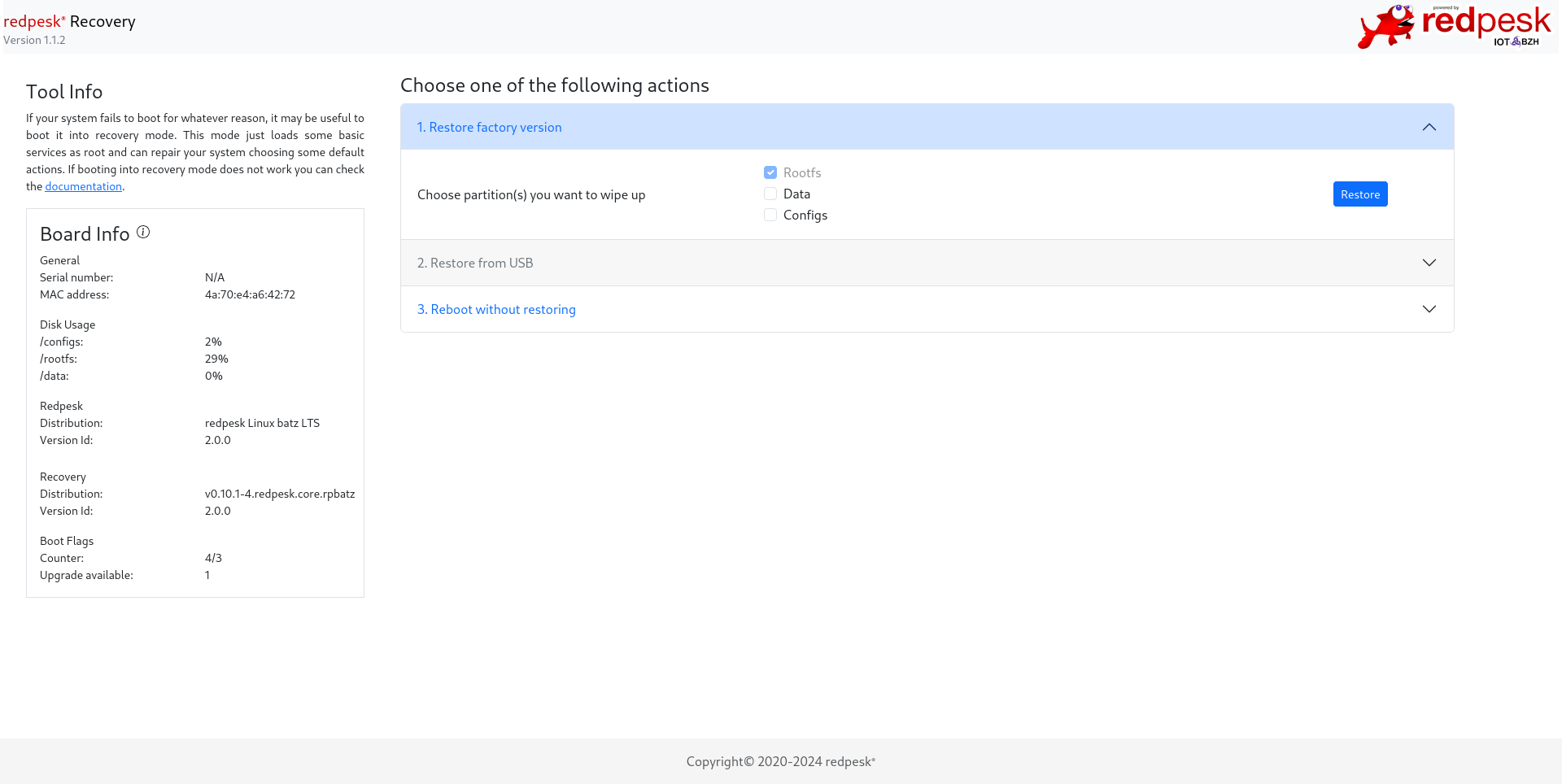
Restoring redpesk OS from factory version
This modes wipes the /rootfs partition then rewrites it with the image which is present in /recovery/backup.tar.gz.
You can choose to recover others partitions such as /data and config if you select these items.
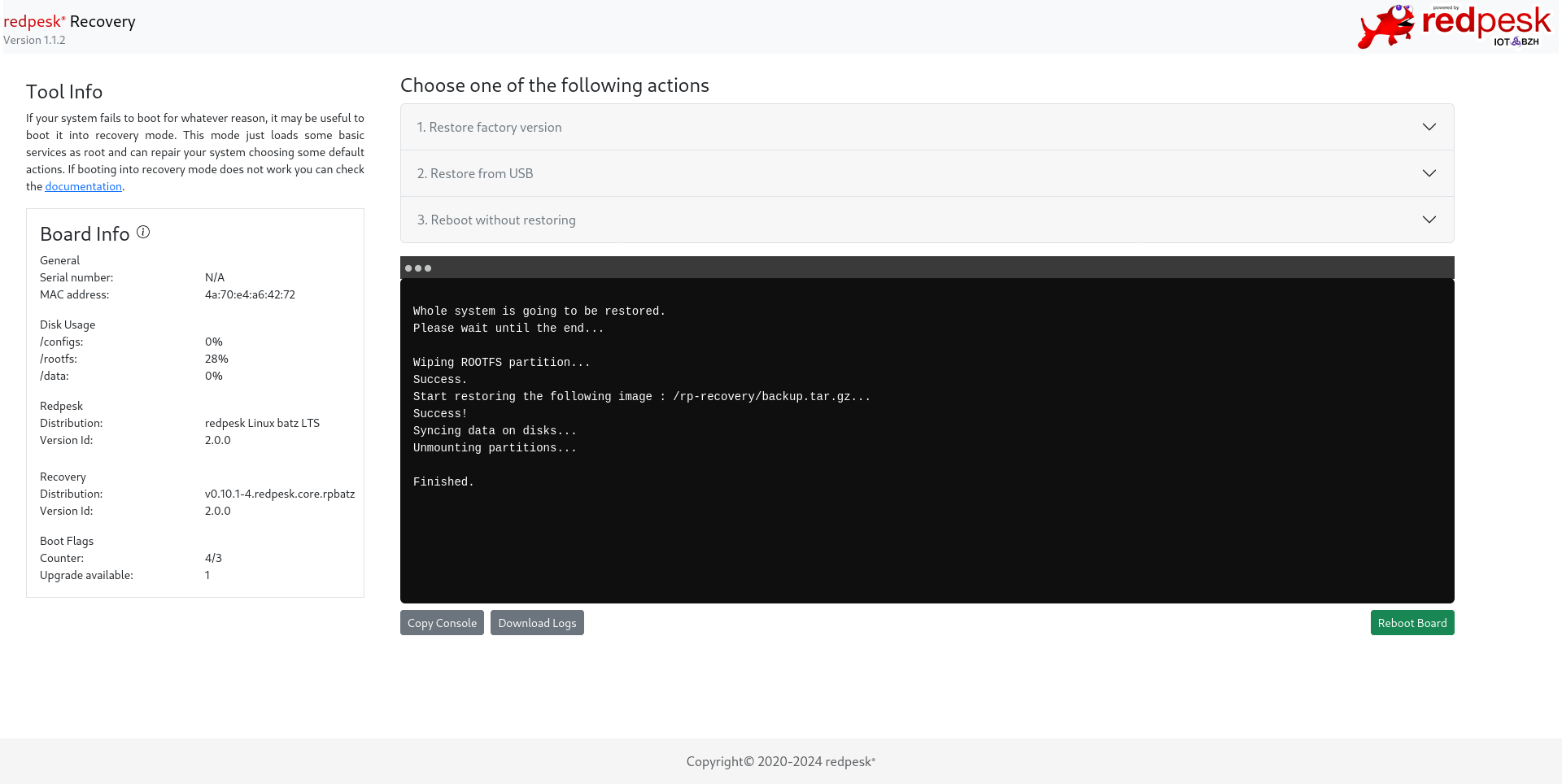
Restoring redpesk from USB
This modes wipes the /rootfs partition then rewrites it with the image which is present in /usb-backup/backup.tar.gz. So you have to create a USB key which will contain this backup tarball as the same output name with the same path when it’s mounted in the initramfs.
NOTE: The recovery mode (initramfs) only supports FAT32 partitions for mounted partitions. So because of FAT32 limitations, your partition label must be named usb-backup that the recovery is looking for.
You can choose to recover others partitions such as /data and config if you select these items.
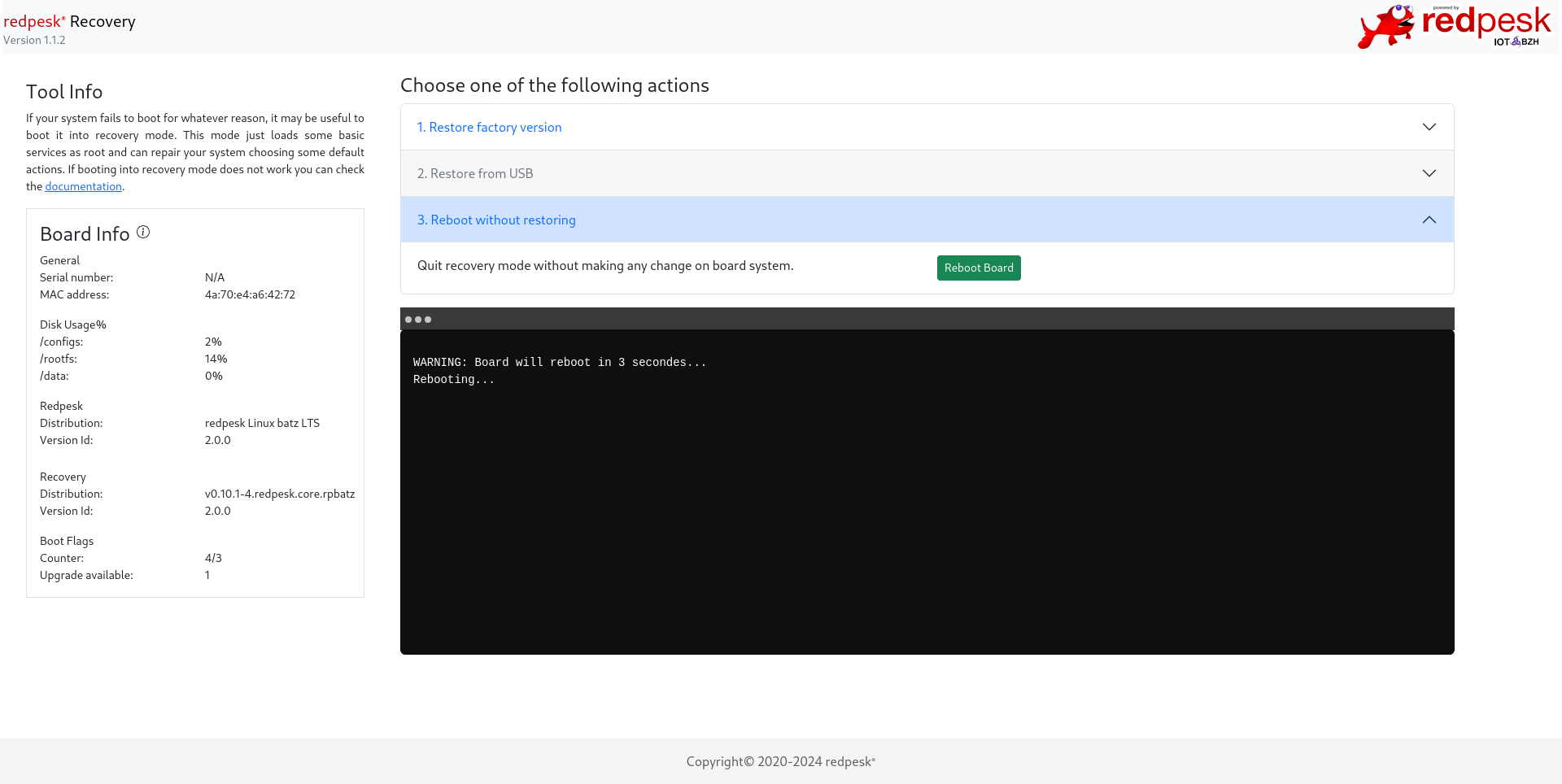
Reboot without restoring
If you want to reboot without redpesk restoration, click on the third menu item:
How to deactivate recovery mode
systemd script to disable U-Boot’s bootcount
A systemd service can be used to call the check-update.sh script to remove the upgrade_available variable in U-Boot’s environment.
Linux kernel watchdog to disable U-Boot’s bootcount
As explained, you should use a watchdog or an equivalent mechanism to decrease the recovery’s variable for each correct boot (e.g. all systemD services correctly started).
It may call the check-update.sh script to remove the upgrade_available variable in U-Boot’s environment.
Please note that you can write into U-Boot’s environment from the Linux userspace by using fw_setenv function from the uboot-tools package.
Force the recovery mode from the bootloader
If you want to directly boot to recovery mode for testing purposes, it is possible to avoid a redpesk OS boot or bootcount variable use. For the most of our boards, we boot redpesk OS on aarch64 (ARM64) boards using U-Boot bootscripts and x86_64 (Intel) boards using GRUB entry menu.
For recovery mode, the alternative bootscript is used to load the initramfs.
load ${devtype} ${devnum}:${distro_bootpart} ${fdt_addr_r} imx8mn-compact.dtb
load ${devtype} ${devnum}:3 ${loadaddr} recovery.img
load ${devtype} ${devnum}:3 ${ramdisk_addr_r} initramfs.img
setenv initrd_size ${filesize}
setenv bootargs console=ttymxc1,115200 rw earlyprintk
booti ${loadaddr} ${ramdisk_addr_r}:${initrd_size} ${fdt_addr_r}
So the only thing to do is to execute it (with defined variables) after interrupting U-Boot bootflow:
Fastboot: Normal
Normal Boot
Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0
# variables for altboot.scr
u-boot=> env set devtype mmc
u-boot=> env set devnum 1
u-boot=> env set distro_bootpart 3
# script load and execution
u-boot=> load mmc 1:1 ${scriptaddr} altboot.scr
u-boot=> source ${scriptaddr}
Useable tool help
As described above, these following scripts are installed on redpesk OS when you install the recovery-tools-binding-scripts package. They are useful for recovery features interaction such as enabling the bootcount variable in the U-Boot bootloader.
- check_board.sh
Usage: check-update.sh [options]
Options:
-r|--reset-flags
Clear all flags
-s|--set-flags
Set flag at the passed value <bootcount,upgrade_available>
Example: --set-flags=0,1 will set upgrade_available to 1 and clear bootcount.
-p|--print-flags
Print actual flags value
-v|--verbose
show debug output messages
default: off
-h|--help
Get this help
- get_board_data.sh
Usage: get_board_data.sh [options]
Options:
--recovery
Get recovery information
--rootfs
Get main rootfs information
--uboot
Get uboot flag data
-a|--all
Get all board available informations
-v|--verbose
Show all output messages
default: off
-h|--help
Get this help
- restore_backup.sh
Usage: restore_backup.sh [options]
Options:
-r|--reboot
Reboot the system
-d|--detect
List available mode according to detected HW configuration
-m|--mode
Available modes are "factory" and "usb"
default: none
-c|--clean
Available partitions are "config", "rootfs" and "data"
default: none
-e|--emulate
Run the script without writing anything on disk
default: on
-f|--force
Force writing on disk
default: off
-v|--verbose
Show all output messages
default: off
-h|--help
Get this help